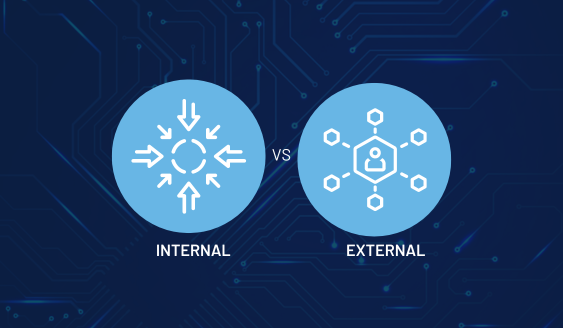
The artificial intelligence revolution is happening faster than most organizations realize. Accordin...
Blog
Blog
Insightful articles, expert tips and inspiring stories from 1Path!
In today's interconnected business environment, cybersecurity isn't just an IT concern—it's a fundam...
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing the way people and businesses operate. From automati...
🛡️Celebrate National Computer Security Day by strengthening your organization’s defenses against cy...
In today's digital world, businesses of all sizes face a growing array of cybersecurity threats. As ...
For small to midsize organizations, it’s difficult to justify the expense of a full-time Chief Infor...
In today’s world, IT services are essential for business operations, from ensuring network security ...
Keeping your operating system (OS) up to date is essential for maintaining optimal performance and s...
Cybersecurity The steady rise in cybersecurity attacks seen in recent years is spreading to all indu...
.jpg?width=100&height=70&name=1path-logo-full-color-rgb-900px-w-300ppi(1).jpg)